
Blog Post
SEO

Nadine
Wolff
published on:
05.02.2020
What is Duplicate Content?
Table of Contents
Duplicate Content (or "duplicate content," "DC") describes the issue where identical or nearly identical content is accessible via multiple URLs or on various pages on the internet. This can include copied sections of text, but also completely identical individual pages. As a result, pages containing duplicate content tend to receive a lower ranking in search results. This is because most search engines conduct a duplicate content check and can effectively recognize and even partially filter out duplicate content.
To ensure your website achieves an optimal ranking, each of your indexed pages should feature unique content, or "unique content." Conducting a duplicate content check and avoiding duplicate content are core tasks of search engine optimization (SEO).
Difference Between Internal and External Duplicate Content
In search engine optimization, a distinction is made between internal and external duplicate content. Below, we'll show you some of many more examples of duplicate content.
Internal Duplicate Content occurs due to identical content that is found under multiple URLs within your own domain. This type of duplicate content often arises from content management systems (CMS) or parameters that automatically structure and create content, such as:
Page with "http" or "https", with or without "www"
Internal search results page
Tag overview page
Filter overview page
Category pages
External Duplicate Content refers to identical content that is available across multiple URLs on different domains. Examples include:
Content theft
Content scraping
Distribution of press releases
Domain migration
Are you planning to move from an old domain to a new domain and want to take the content with you? The last point, domain migration, can be resolved with a simple 301 redirect.
How Do I Find Duplicate Content? – Duplicate Content Check
The simplest way to identify DC is by entering text excerpts into the search engine. However, it can be done more easily using tools like Google Search Console. In the free Search Console, there is the "Index Coverage" report, where Google lists pages identified as duplicates.
[caption id="attachment_25336" align="aligncenter" width="789"]

Fig. 1 Index Coverage - Identify Duplicates in Google Search Console[/caption]
With one click on "Duplicate – submitted URL not set as canonical," you get an overview of all URLs classified as duplicate content (Fig. 2). This allows you to specifically revise and optimize pages that have duplicate content.
[caption id="attachment_25338" align="aligncenter" width="694"]
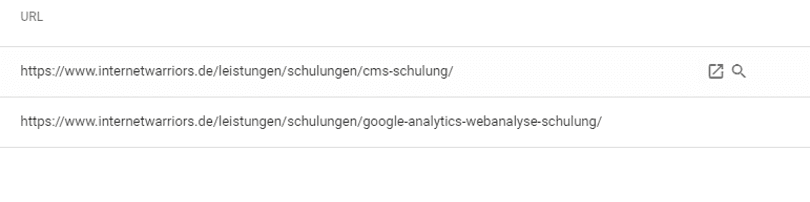
Fig. 2 URLs of Duplicates in Google Search Console[/caption]
How Do Search Engines Identify Duplicate Content?
Search engines like Google identify and filter duplicate content during scheduling, indexing, and in the search results of the crawling and indexing process.
[caption id="attachment_25334" align="aligncenter" width="625"]
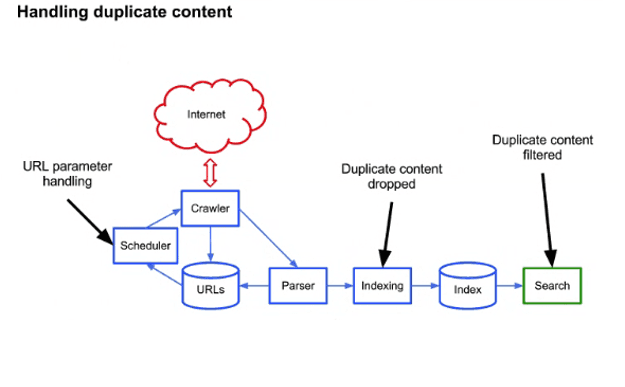
Fig. 3 Duplicate Content in the Crawling Process[/caption]
Duplicate Content - URL Parameters
The concept of a URL is that it is always supposed to be a unique address of a resource on a server. Unique URLs with parameters but the same content are a classic case of duplicate content.
Solution via rel="canonical"
Using a canonical tag, URLs with parameters can refer to a main or overview page. Most content management systems have plugins that set the rel="canonical" tag, which is easily readable by search engines.
Solution via "noindex"
Another solution, which can be implemented through CMS plugins, is to set a meta robots tag to "noindex" in the <head> of the page. The "noindex" command tells the search engine not to include this URL or page in the index.
It should be noted that these two solutions should not be combined according to Google guidelines (John Mueller)!
Search Engines Filter Duplicate Content
If duplicate content is found on your page and has been indexed by the search engine, Google can filter it. Filtering duplicate content means the search engine systematically ignores or hides the content affected by DC. This reduces the overall readable content and degrades its relevance and ranking in search results. In SEO, a word count of at least 400-800 words is recommended, sometimes even more depending on the competitor comparison. Don't let duplicate content affect your ranking and visibility!
Tips to Avoid Duplicate Content
Below we offer you a series of tips to avoid duplicate content:
Unique URL per content
Avoid URL variations
Topically distinct page
Topically appropriate internal linking
Avoid repetitive text blocks
Use tools like Google Search Console
Merge very similar content into one URL
Links to topically relevant and appropriate pages within a domain even strengthen your internal linking. Using internal linking, topic clusters can be created that search engines recognize and appropriately display in search results. Google Guidelines provide additional guidance and help on "avoiding duplicate content."
Create Unique Content
In editorial SEO, creating unique content, or unique content, that fulfills users' search intentions is a top priority. Ensure that users find relevant and unique content on your site and stay on your site. However, most companies lack the necessary resources to engage in content marketing.
Content marketing, as well as content optimization, is a strong area of expertise for internetwarriors. If you need support in creating SEO-optimized content, feel free to contact us for free!

Nadine
Wolff
As a long-time expert in SEO (and web analytics), Nadine Wolff has been working with internetwarriors since 2015. She leads the SEO & Web Analytics team and is passionate about all the (sometimes quirky) innovations from Google and the other major search engines. In the SEO field, Nadine has published articles in Website Boosting and looks forward to professional workshops and sustainable organic exchanges.


