
Blog Post
Web Analytics

Nadine
Wolff
published on:
20.08.2015
Chrome, Safari, Internet Explorer, or Firefox? The small, subtle differences.
Table of Contents
Following a brief mention of the topic: Browser Architecture in the last article, this article will explain how a browser is structured, what it needs to be able to do, and how it is tested. Additionally, there is a brief overview of the latest versions of the browsers discussed in this article.
What a Browser Needs to Have:
The browser is one of the most important software programs on a computer. It is considered the gateway to the internet. Consequently, the demands on a browser are increasing. The core point of a browser is: information must be displayed quickly and securely.
The following factors are highly important for users:
Ease of use
Speed
Modern standards like HTML 5
Modern user interface
Plugins / Extensions / Add-ons
Security
The browser must have one main function: to display the web resource that is called from the server and shown in the web window.
It can generate HTML documents as well as display PDF files, images, and other formats. Every browser has a high-level structure. This includes, among others, the user interface with its address bar, the bookmarks menu, and other components. Moreover, a rendering module for content display and a JavaScript interpreter are part of it. These and many other components describe the architecture of a browser.
The most well-known browsers are Microsoft’s Internet Explorer, Apple’s Safari, Mozilla’s Firefox, and Google’s Chrome.
Browser Benchmarks
As soon as a new version of a browser is released, so-called browser benchmarks are created. Benchmarks are specific tools used to test the performance of browsers.
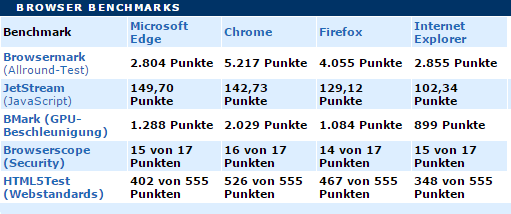
Benchmark test from www.chip.de (16.8.2015)
In this test, the Safari browser is completely ignored. Instead, the new Microsoft browser Edge is tested, also to show the differences between Microsoft’s two current browsers.
“Browsermark” is a benchmark for mobile and smartphone browsers. This tool compares mobile browsers independently of the connection technology used.
A JavaScript benchmark checks whether modern and complex web applications can be implemented by the respective browsers. In this case, the benchmarking tool “JetStream” is used.
With GPU acceleration, graphics processor-accelerated calculations are primarily scrutinized using “BMark.”
The security test is realized with “Browsescope.” This offers a collection of security tests that can determine if the tested browser supports JavaScript APIs in a way that enables secure interaction between websites and adheres to best practices in blocking harmful sites.
With “HTML5-Test,” a browser’s compatibility with the latest HTML5 web standards is checked. Examples include video and MP3 playback.
A quick glance at the table makes it clear who comes out on top. Chrome wins due to its exciting features and speed. However, the competition is rapidly catching up. Below is a quick overview of all the latest browsers and their updates.
Firefox 40
Security is a top priority at Mozilla. Add-ons can be useful but may also contain malware. A remedy for this is an in-store activated extension to adhere to certain rules, the so-called add-on guidelines.
Furthermore, according to its own statements, Mozilla has built in protection against unwanted downloads, implemented smoother scrolling on web pages with VSync, and optimized memory usage and loading time of JPEG graphics.
Chrome 44
A major plus for Google Chrome is its integration with Google services like Gmail, Maps, or Docs. For this reason, version 43 fixed 43 security bugs. Google also stated that they collaborated with external security researchers here.
An improved rendering algorithm is supposed to enhance video playback. Additionally, shortcuts can now be placed directly on the taskbar.
Safari 8.0
A new version of the Safari browser always offers new visual updates. In this case, the design is very much aligned with the new OS for Mac: OS X Yosemite.
The new tab view with thumbnail windows is practical. These are displayed in the Safari browser from a kind of bird's eye view. Safari offers integrated use for the DuckDuckGo search engine. Unlike other examined search engines, this one promises not to track search queries.
The browser now also supports HTML5 Premium Video Extensions, allowing, for example, Netflix HD videos to be watched for two hours longer.
Internet Explorer Version 11
Even with fresh versions, updates for Internet Explorer are frugally managed. At the most, new browser functions come with a new Windows version.
The design of IE has hardly changed. The browser works with menus, submenus, and sub-submenus. Also, the competition surpasses Internet Explorer in terms of speed and performance.
But Microsoft has an ace up its sleeve. With Windows 10, a new browser will hit the market: Microsoft Edge. Besides a neat and modern design, new browser technologies are expected to bring more speed and security.
Ultimately, personal taste decides which browser makes surfing the vast World Wide Web most enjoyable.
Is your website displayed differently in Chrome compared to Safari? We would be happy to advise you and identify the issues. We ensure optimal presentation in all current browsers and on all mobile devices. Contact us!

Nadine
Wolff
As a long-time expert in SEO (and web analytics), Nadine Wolff has been working with internetwarriors since 2015. She leads the SEO & Web Analytics team and is passionate about all the (sometimes quirky) innovations from Google and the other major search engines. In the SEO field, Nadine has published articles in Website Boosting and looks forward to professional workshops and sustainable organic exchanges.


