
Blog Post
SEO

Nadine
Wolff
published on:
20.07.2017
CAPTCHAs – a necessary evil in our daily internet activities
Table of Contents
You are probably familiar with the following situation: When leaving a comment on a blog page, you need to prove that you are not a machine. To do this, you must undergo a sort of test – a CAPTCHA.
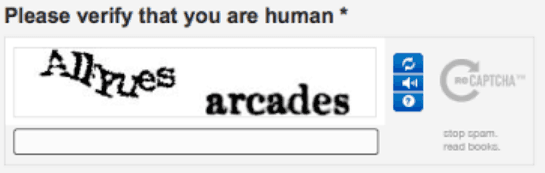
Some are simple arithmetic operations that need to be solved to submit comments or form requests. Another form is the correct transcription of an alphanumeric combination, often presented as an image.
This article explores what CAPTCHAs are, why this method is indispensable today, and the challenges they bring.
Many internet users have long found CAPTCHAs to be annoying and a waste of time. There was a concern that CAPTCHAs could limit visitor access and even cause them to leave altogether. Today, we recognize the positive aspects and importance of CAPTCHAs. But what exactly are these CAPTCHAs?
The significance of CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHA stands for "Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart." It is essentially a response test that determines whether a user on a website is a human or a machine. CAPTCHAs were invented in 1997, initially in the form of a distorted image. The distorted image conceals the message from machine interpretations. CAPTCHAs are primarily used for security purposes. However, the effectiveness of this method is now questioned, as modern bots can bypass CAPTCHA security measures, leading to various kinds of spam activities.
The basic idea of the Turing Test
The so-called Turing Test was developed by the English mathematician, computer scientist, and cryptanalyst Alan Turing. The test demonstrates a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior. It involves a human evaluator who judges a conversation between a human and a machine. The human evaluator is aware that one of the participants is a machine. If the machine successfully mimics a human, the test is passed.
Why CAPTCHAs are used
CAPTCHA technology is employed to block spam activities and bots that attempt to collect various email addresses mechanically or automatically register on different websites, blogs, forums, etc. CAPTCHA aims to block these forms of automated systems.
Interestingly, the algorithm for this human-machine test is publicly accessible.
CAPTCHAs are primarily based on tasks involving reading and interpreting displayed text or tasks that require visual perception. These requirements often prevent visually impaired users from accessing such websites. Audio interpretations of text and speech recognition software are used to enable visually impaired individuals to solve CAPTCHAs more easily.
The downsides of CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHAs have faced criticism, particularly due to their distorted images that exceed many people's understanding. These problems are especially challenging for those with visual or hearing impairments. The time taken to solve a CAPTCHA can be frustrating and slow down the work process.
Google's reCAPTCHAs
Invisible CAPTCHAs are the latest development in the "Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart." Google acquired reCAPTCHA in 2009. In 2013, the system was updated to the well-known "I'm not a robot" checkbox.
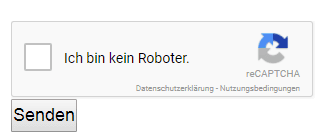
This version works by determining the realistic user of the website through their clicking style. If the clicking style seems inaccurate and unnatural, another test will be given. However, the Invisible CAPTCHA can determine whether the user is human or machine by analyzing browser behavior.
Conclusion
This article discusses the pros and cons of CAPTCHAs. It raises the question, are CAPTCHAs less of a problem and more of a solution? CAPTCHAs provide extensive protection and should not be viewed only as annoying and disruptive.
We recommend integrating a CAPTCHA in the contact form of your website or in the comment form. Contact us and we will assist you with the implementation.

Nadine
Wolff
As a long-time expert in SEO (and web analytics), Nadine Wolff has been working with internetwarriors since 2015. She leads the SEO & Web Analytics team and is passionate about all the (sometimes quirky) innovations from Google and the other major search engines. In the SEO field, Nadine has published articles in Website Boosting and looks forward to professional workshops and sustainable organic exchanges.
no comments yet


