
Blog Post
SEO

Nadine
Wolff
published on:
08.11.2011
Search Engine Optimization for International Websites Part 1: Domain Strategy
Table of Contents
It is a challenge faced by every expanding company presenting itself on the internet: How do you optimize a portfolio of international websites for search engines and visitors? What strategies make sense and what considerations should be included in the planning? We have compiled the key points. This is Part 1 of the three-part post series on SEO for international websites.
TLDs, Subdirectories, or Subdomains
A concept should be developed as the basis of the international domain strategy that determines which websites will present the country-specific content. Generally, three different solutions are recommended:
1. Top-Level Domains (TLD) (e.g., www.domainname.de)
In the respective country-specific search engines, the top-level domains usually achieve the best results. This solution is also sensible for usability reasons because the user encounters a familiar domain structure and is likely to remember the domain name better than a subdomain or directory. This option is also suitable for companies whose various international domains differ significantly in their structure and products. Another advantage from an SEO perspective is the ability to host each domain in the respective country with a suitable IP address, thereby increasing the chance of ranking in that country.
The disadvantages of this solution include the increased effort required for marketing a new domain. Content and links require resources for each domain that should not be underestimated, as a new country-specific domain does not benefit from the backlinks to the main domain, so link building practically starts from scratch.
In summary, this option is often preferable to the other strategies, particularly if it is a strong brand and resources are available to manage each domain separately. In some countries, it is also challenging to register a specific TLD without having a postal address in that country. Ideally, there should also be country-specific contacts for each domain.
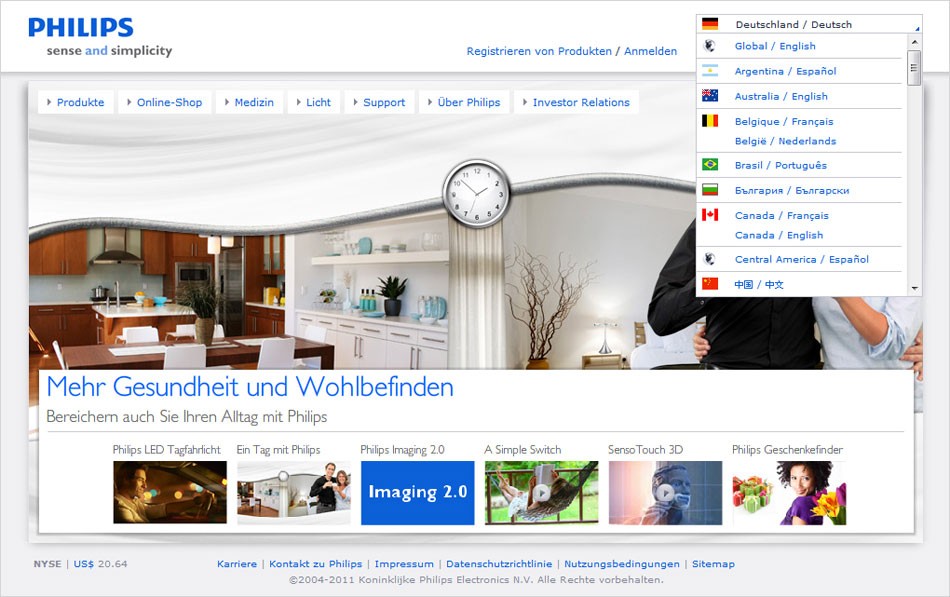
Philips resolves its international domains via country-specific TLDs
2. Subdomains (e.g., de.domainname.com)
Subdomains are considered similarly to an independent top-level domain by Google. Through geotargeting in the Google Webmaster Tools, they can be assigned to a country or region. Subdomains can also be locally hosted.
Disadvantages can also be identified for this solution. The main domain passes only minimal trust to the subdomain, so link building also involves effort here. Additionally, the address structure is not very intuitive, as most users are familiar with the URL as www.domainname.de. There is also a risk that many links will point to the respective TLD. If the subdomain route is chosen, it is advisable to set up at least a permanent redirect via the most important TLDs to direct users who enter this to the correct website.
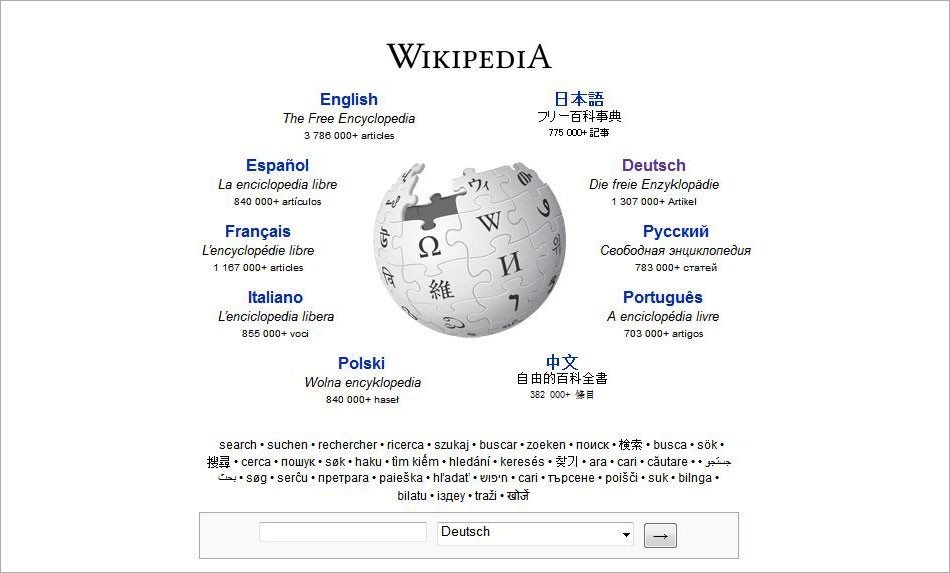
The most well-known example of the subdomain solution is certainly Wikipedia
3. Directory (e.g., www.domainname.com/de/)
The clear advantage of directories is their simple management. Like subdomains, individual directories can also be assigned to a country using geotargeting in the Google Webmaster Tools. Trust is automatically passed on to the directory with this solution. All links to the domain or one of the directories also strengthen the entire domain.
The biggest disadvantage with this strategy is the lower relevance for country-specific target markets, as Google values the appropriate TLDs more highly. For similar content for different countries with the same language (for example, the UK and the USA, or Germany and Austria), there can also be a duplicate content problem. Additionally, with this solution, it is not possible to host the country-specific pages in the respective country.
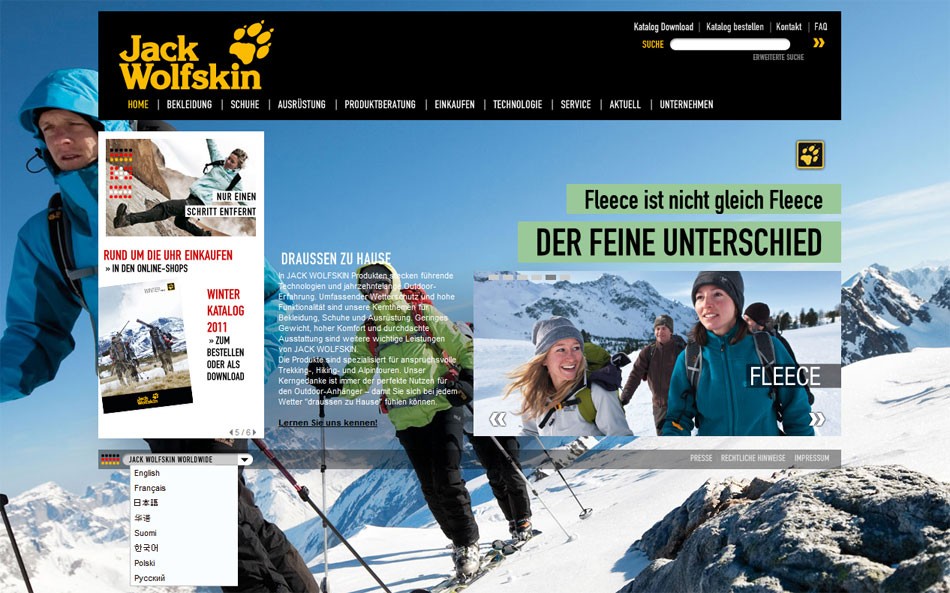
Jack Wolfskin resolves country-specific pages via directories
Google Webmaster Tools: Geotargeting
In the Google Webmaster Tools, you can set under the "Geographic target" setting which country or region a website, subdomain, or directory is assigned to. Not all countries are available, but the most important European and non-European countries are. This measure does not replace all other optimization measures described here, but it gives the search engine a hint about the target country or region.
Hosting
As mentioned above, a domain should ideally be hosted in the target country. This is particularly important when a generic TLD like .com or .org is used. Although it is recommended to host a country-specific TLD in the respective country (a .de domain for the German market should, for example, be hosted in Germany), it is less important because Google uses the TLD as the main signal for localizing the website. With a generic TLD, the hosting location carries more weight, assigned based on the IP address.

Nadine
Wolff
As a long-time expert in SEO (and web analytics), Nadine Wolff has been working with internetwarriors since 2015. She leads the SEO & Web Analytics team and is passionate about all the (sometimes quirky) innovations from Google and the other major search engines. In the SEO field, Nadine has published articles in Website Boosting and looks forward to professional workshops and sustainable organic exchanges.


