
Blog Post
Web Analytics

Halid
Osmaev
published on:
06.12.2023
Server-Side Espionage - An Overview of the User Data Sent
Table of Contents
Server-Side Tracking is gaining increasing relevance. This is especially true with the upcoming update in Chrome, where third-party cookies will be blocked (see here[Intent to Deprecate & Remove: Third-Party Cookies (google.com)]). One often mentioned advantage is the control over data flow that is ensured, especially user data. In this article, we explore the topic of server-side tracking with Google Tag Manager and discuss what user data is transmitted.
But first, the important question:
What is server-side tracking?
We will undertake a detailed examination of the implementation using Google Tag Manager to gain a deeper understanding of these processes. In traditional tracking, a code snippet is embedded in the page, possibly through Google Tag Manager, and this sends the event data directly to third-party services like Google Analytics 4, Meta Ads, etc.
During this process, the control over the transmitted user data (IP address, demographic data, etc.) is limited to the adjustments offered by the tool.
Furthermore, a third-party cookie is usually set, resulting in a loss of quality and quantity of our tracking data.
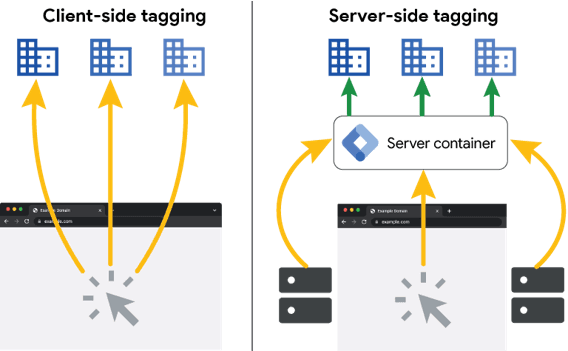
Figure 1: Comparison of client-side and server-side tagging
In server-side tracking, however, all data is first sent to a dedicated server running the server-side Google Tag Manager. This ensures that there is no unwanted data transfer happening on the user's side of the website. This transfer occurs first within the server-side Google Tag Manager. This process can then be tailored to meet privacy-compliant standards through clear data insights and additional configuration options, such as transformers.
Additionally, the data request is treated similarly to an API request to your own server, making it less likely to be blocked. By ensuring data transmission takes place exclusively within your own server infrastructure, potential risks related to data protection authorities can be minimized.
Furthermore, various data protection laws play an important role. The most significant are the GDPR, the TTDSG, and the EU-US agreement.
Here is a summary of their content:
GDPR:
No user data may be collected without consent through a cookie banner. The mentioned user data refers to data enabling identification of a real person (email, phone, name, etc.).
TTDSG:
No data may be collected without the user's consent.
EU-US Agreement:
Previously, sending data to the USA was problematic as the government could access data at any time by law. This law has made data transmission to US services less concerning.
These are just some of the laws affecting tracking. Therefore, understanding user data is crucial.
What user data is sent to the server-side Google Tag Manager?
The good news: The absolute minimum.
What does this mean? When an event, like a click, is triggered on the page, an HTTP request is sent to the server-side Google Tag Manager. Of course, this includes the information of an HTTP header.
This includes, among other things:
Time
IP Address
Page URL
Approximate location (through IP address)
Operating System
Browser
Resolution
Device
Additionally, there are other parameters specifically related to the configuration. For detailed information, the documentation under [https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers] can be consulted.
Moreover, there are parameters automatically captured by Google Tag for campaign optimization. These include:
utm_source
utm_medium
utm_campaign
utm_content
utm_term
and the Click ID
It should continue to be noted which data is transmitted with user-defined configuration in Google Tag Manager.
In the server-side Google Tag Manager, users can specifically configure using transformers to determine which specific data should be forwarded in which form and which should be retained.
For secure data implementation, however, the conclusion should be:
“Track only as much data as is necessary.”
Limiting tracking to essential data without putting oneself at a disadvantage is the challenge here.
Internetwarriors are an expert team in web analytics and server-side tracking (SST). With comprehensive expertise and a deep understanding of the latest trends and technologies in digital analytics, the Internetwarriors offer tailored solutions to optimize their customers' online presence, making them a valuable partner for anyone looking to enhance their web analysis capabilities.
Get in contact with us!

Halid
Osmaev
Halid Osmaev has been with the internetwarriors in web analytics since August 2021. With extensive knowledge in IT and mathematics, he can assist you with everything from simple to the most complex web analytics topics. Whether it's setting up a basic tracking infrastructure or conducting an in-depth analysis of company processes, he's ready to help.


